Bioflix activity cellular respiration food as fuel – In this comprehensive exploration of Bioflix Activity: Cellular Respiration: Food as Fuel, we delve into the intricate mechanisms that sustain life, unraveling the process by which food is transformed into the energy that powers our cells. This scientific journey promises to illuminate the fundamental principles of cellular respiration, empowering us with a deeper understanding of the biological processes that govern our very existence.
Cellular respiration, the cornerstone of energy production in living organisms, is a complex biochemical pathway that converts food into ATP, the universal energy currency of cells. This intricate process involves the breakdown of glucose, the primary energy source for cells, through a series of enzymatic reactions.
As we explore the intricacies of cellular respiration, we will uncover the role of the electron transport chain, a crucial component responsible for generating ATP. Additionally, we will examine anaerobic respiration, an alternative pathway employed by cells in the absence of oxygen.
Cellular Respiration Overview

Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. This process is essential for the survival of all living organisms because ATP serves as the main energy currency for cells.
Cellular respiration occurs in three main stages:
- Glycolysis: The breakdown of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate.
- The Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle): The further breakdown of pyruvate into carbon dioxide and energy-rich molecules.
- Oxidative phosphorylation: The generation of ATP through the electron transport chain.
Cellular respiration can be summarized by the following equation:
C 6H 12O 6(glucose) + 6O 2(oxygen) → 6CO 2(carbon dioxide) + 6H 2O (water) + energy (as ATP)
ATP is used to power a variety of cellular processes, including muscle contraction, protein synthesis, and nerve impulse transmission.
Food as Fuel: Bioflix Activity Cellular Respiration Food As Fuel
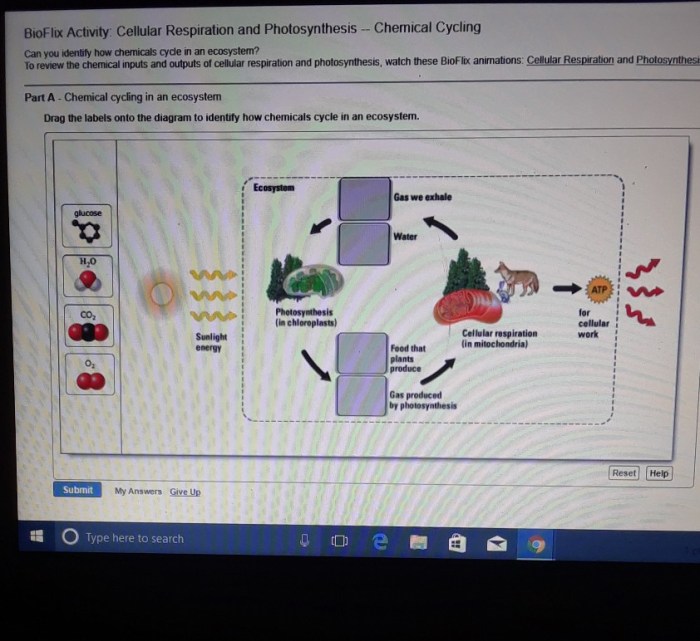
The primary fuel for cellular respiration is glucose, a simple sugar that is broken down into smaller molecules to release energy.
Other types of food molecules, such as fats and proteins, can also be used as fuel for cellular respiration. However, these molecules must first be converted into glucose through a process called catabolism.
The breakdown of food molecules into glucose is facilitated by enzymes, which are proteins that act as catalysts for specific chemical reactions.
The Electron Transport Chain
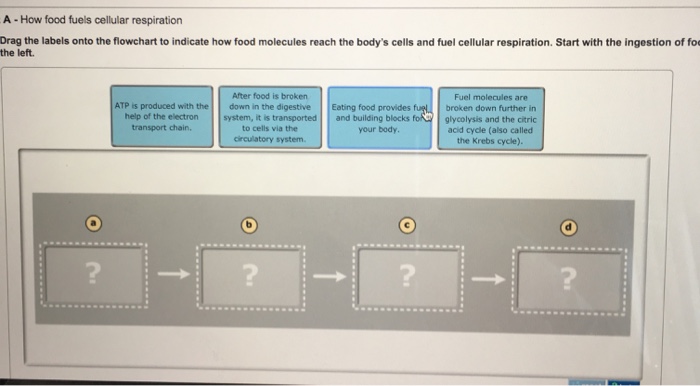
The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes located in the inner membrane of mitochondria. These complexes pass electrons from one to another, generating a proton gradient across the membrane.
The proton gradient is used to drive the synthesis of ATP through a process called oxidative phosphorylation.
Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain. Without oxygen, the electron transport chain cannot function and ATP cannot be produced.
Anaerobic Respiration
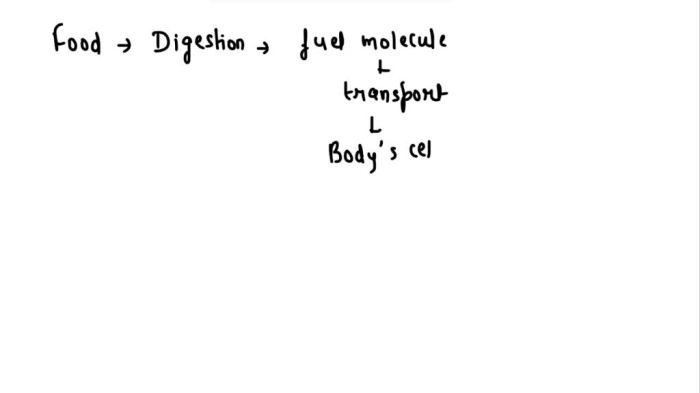
Anaerobic respiration is a type of cellular respiration that does not require oxygen. This process occurs in some bacteria and yeast, as well as in human muscle cells during intense exercise.
In anaerobic respiration, glucose is broken down into lactic acid or ethanol, rather than carbon dioxide and water. This process generates less ATP than aerobic respiration.
Fermentation is a type of anaerobic respiration that occurs in yeast and bacteria. In fermentation, glucose is broken down into ethanol and carbon dioxide.
Answers to Common Questions
What is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic reactions that convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products.
What is the role of food in cellular respiration?
Food provides the organic molecules that are broken down to produce ATP through cellular respiration.
What is the electron transport chain?
The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes that transfer electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen, generating a proton gradient that is used to produce ATP.
What is anaerobic respiration?
Anaerobic respiration is a type of cellular respiration that does not require oxygen and produces ATP through the fermentation of glucose.