Introducing Section 4.3 Modern Atomic Theory Answer Key, a definitive resource that unlocks the intricacies of modern atomic theory. This comprehensive guide delves into the historical significance, key concepts, and practical applications of this foundational scientific framework.
Delving into the depths of atomic structure, electron configuration, and periodic trends, this guide provides a thorough understanding of the fundamental building blocks of matter. It explores the different types of chemical bonding, their implications, and the relationship between electron configuration and bonding behavior.
1. Introduction to Section 4.3 Modern Atomic Theory
Section 4.3 of modern atomic theory marks a significant milestone in the evolution of our understanding of the structure of matter. It introduced the concept of the atom as a composite entity, composed of even smaller particles known as protons, neutrons, and electrons.
This breakthrough revolutionized our understanding of the fundamental building blocks of the universe.
This section covers key concepts such as atomic structure, electron configuration, periodic trends, and chemical bonding. These concepts form the foundation for comprehending the behavior of elements and their interactions with each other.
2. Atomic Structure
Structure of an Atom
An atom consists of a dense, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons, while the electrons occupy specific energy levels around the nucleus.
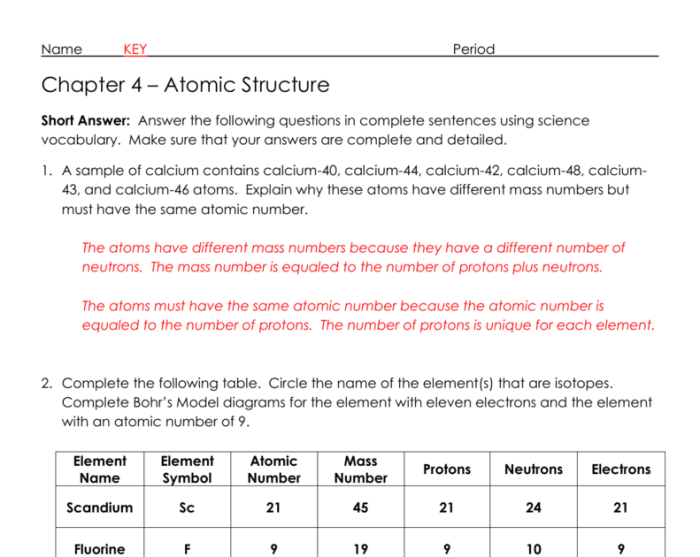
Atomic Number and Mass Number
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in its nucleus, which determines its identity. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different mass numbers. They have varying numbers of neutrons and exhibit distinct physical and chemical properties.
3. Electron Configuration: Section 4.3 Modern Atomic Theory Answer Key
Concept of Electron Configuration, Section 4.3 modern atomic theory answer key
Electron configuration describes the distribution of electrons in the various energy levels and orbitals around the nucleus. It plays a crucial role in determining an element’s chemical properties.
Rules for Determining Electron Configuration
The rules for determining electron configuration include the Pauli exclusion principle, Hund’s rule, and the Aufbau principle. These rules govern the number of electrons in each energy level and their spin orientations.
Electron Configurations of Various Elements
The electron configurations of various elements can be determined using the periodic table. This information helps predict their chemical reactivity and bonding behavior.
4. Periodic Trends

Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties
Elements exhibit periodic trends in their atomic properties, such as atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity. These trends can be explained based on the number of electrons and the distance from the nucleus.
Reasons for Periodic Trends
The periodic trends in atomic properties are primarily due to the increasing atomic number and the varying shielding effect of inner electrons. These factors influence the size, charge, and reactivity of atoms.
Table of Periodic Trends
| Property | Trend |
|---|---|
| Atomic Radius | Decreases from left to right across a period |
| Ionization Energy | Increases from left to right across a period |
| Electronegativity | Increases from left to right and bottom to top |
5. Chemical Bonding

Types of Chemical Bonding
Chemical bonding involves the interaction between atoms to form stable compounds. The three main types of chemical bonding are ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding.
Examples of Compounds Formed by Each Type of Bonding
- Ionic: NaCl (sodium chloride)
- Covalent: H 2O (water)
- Metallic: Fe (iron)
Relationship between Electron Configuration and Chemical Bonding
The electron configuration of an element determines its bonding behavior. Elements with similar electron configurations tend to form similar types of bonds.
FAQ Corner
What is the historical significance of Section 4.3 in the development of modern atomic theory?
Section 4.3 builds upon the groundbreaking work of Niels Bohr and others, refining and expanding our understanding of atomic structure and behavior.
How does electron configuration influence chemical bonding?
Electron configuration determines the number and arrangement of valence electrons, which play a crucial role in the formation and properties of chemical bonds.
What are the key periodic trends and how are they explained?
Periodic trends describe the systematic variations in atomic properties across the periodic table and can be explained based on atomic structure and electron configuration.