The graphic organizer branches of government is a visual representation of the structure and functions of the three branches of the U.S. government: the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. This framework, established by the U.S. Constitution, ensures a balance of power among the branches and prevents any one branch from becoming too powerful.
The executive branch, led by the President, is responsible for enforcing laws, conducting foreign policy, and managing the federal bureaucracy. The legislative branch, consisting of the House of Representatives and the Senate, has the power to make laws, declare war, and impeach the President.
The judicial branch, headed by the Supreme Court, interprets laws and determines their constitutionality.
Executive Branch
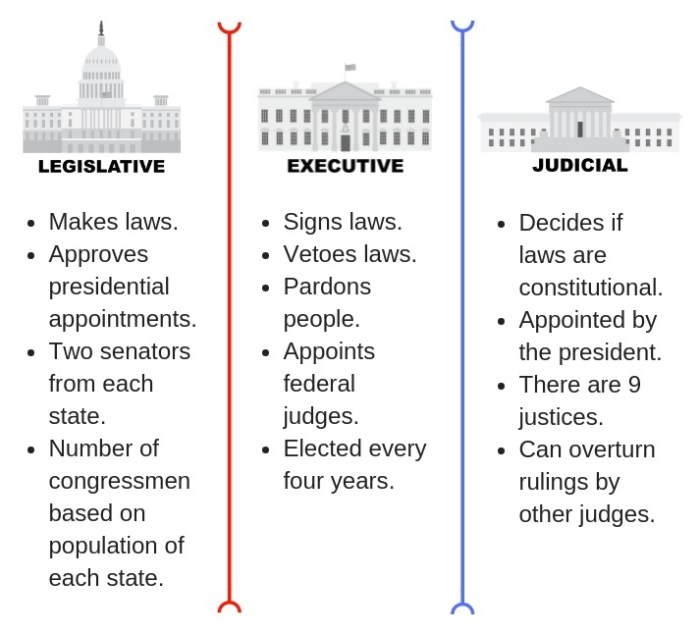
The Executive Branch is headed by the President of the United States, who is both the head of state and the head of government. The President is responsible for carrying out the laws of the United States and for representing the country abroad.
Role and Responsibilities of the President
- Enforce the laws of the United States
- Serve as Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces
- Conduct foreign policy
- Appoint and remove federal officials
- Veto legislation passed by Congress
Powers and Limitations of the President
- Powers:Commander-in-Chief, veto power, appointment power
- Limitations:Can be impeached by Congress, subject to checks and balances
Structure and Functions of the Executive Office of the President
The Executive Office of the President (EOP) is a group of advisors and staff that helps the President carry out his duties. The EOP includes the White House Office, the National Security Council, and the Office of Management and Budget.
Legislative Branch
The Legislative Branch is responsible for making laws. It is composed of the Senate and the House of Representatives.
Role and Responsibilities of Congress
- Make laws
- Declare war
- Raise taxes
- Approve treaties
- Impeach the President
Powers and Limitations of Congress, Graphic organizer branches of government
- Powers:Make laws, declare war, raise taxes
- Limitations:Can be vetoed by the President, subject to checks and balances
Structure and Functions of the House of Representatives and the Senate
The House of Representatives is composed of 435 members, each of whom is elected from a single district. The Senate is composed of 100 members, each of whom is elected from a state.
Judicial Branch
The Judicial Branch is responsible for interpreting the laws of the United States. It is composed of the Supreme Court, the federal courts of appeals, and the federal district courts.
Role and Responsibilities of the Supreme Court
- Interpret the Constitution
- Review laws passed by Congress
- Decide cases involving federal law
Powers and Limitations of the Supreme Court
- Powers:Judicial review, interpret the Constitution
- Limitations:Decisions can be overturned by constitutional amendments
Structure and Functions of the Federal Court System
The federal court system is composed of three levels: the Supreme Court, the federal courts of appeals, and the federal district courts. The Supreme Court is the highest court in the United States.
Checks and Balances: Graphic Organizer Branches Of Government
The system of checks and balances is designed to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful. Each branch of government has the ability to check the power of the other two branches.
Purpose and Effectiveness of Checks and Balances
- Purpose:Prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful
- Effectiveness:The system of checks and balances has been effective in preventing any one branch of government from becoming too powerful.
Examples of How Checks and Balances Have Been Used in Practice
- The President can veto legislation passed by Congress.
- Congress can override a presidential veto with a two-thirds vote.
- The Supreme Court can declare laws passed by Congress to be unconstitutional.
Separation of Powers
The principle of separation of powers is designed to prevent any one person or group from having too much power. The three branches of government are separate and independent, and each branch has its own powers and responsibilities.
Benefits and Challenges of Separation of Powers
- Benefits:Prevents any one person or group from having too much power
- Challenges:Can lead to gridlock and inefficiency
Examples of How Separation of Powers Has Been Implemented in the U.S. Government
- The President is the head of the Executive Branch.
- Congress is the head of the Legislative Branch.
- The Supreme Court is the head of the Judicial Branch.
FAQ Explained
What is the purpose of the graphic organizer branches of government?
The graphic organizer branches of government is a visual representation of the structure and functions of the three branches of the U.S. government. It helps students and citizens alike understand the complex system of checks and balances that ensures the stability and longevity of American democracy.
What are the three branches of government?
The three branches of government are the executive branch, the legislative branch, and the judicial branch.
What is the role of the executive branch?
The executive branch, led by the President, is responsible for enforcing laws, conducting foreign policy, and managing the federal bureaucracy.