Ap psych motivation and emotion – In the realm of AP Psychology, motivation and emotion stand as inseparable forces that shape our behavior and experiences. This article delves into the captivating world of these psychological concepts, exploring their definitions, theories, and applications in a manner that is both accessible and thought-provoking.
Through the lens of biological, psychological, and social perspectives, we will unravel the intricacies of motivation, uncovering the driving forces behind our actions. We will also delve into the fascinating realm of emotions, examining the physiological and psychological processes that underpin our emotional responses.
Defining Motivation and Emotion

Motivation and emotion are two essential psychological concepts that influence our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Motivation drives us to act, while emotions color our experiences and shape our interactions with the world.
Motivation, Ap psych motivation and emotion
Motivation refers to the psychological processes that energize and direct our behavior. It involves the internal and external factors that influence our desires, goals, and actions. Key characteristics of motivation include:
- Direction:Motivation gives our behavior a sense of purpose and direction, guiding us towards specific goals.
- Intensity:The strength of our motivation determines the level of effort and persistence we put into our actions.
- Persistence:Motivation helps us maintain our efforts even in the face of obstacles and challenges.
Emotion
Emotion is a complex psychological state that involves subjective feelings, physiological changes, and behavioral expressions. It arises in response to internal or external stimuli and serves various functions, including:
- Communication:Emotions convey our feelings and intentions to others, facilitating social interactions.
- Adaptation:Emotions help us adapt to our environment by guiding our behaviors towards positive outcomes and away from threats.
- Motivation:Emotions can motivate us to act or inhibit certain behaviors, influencing our decision-making and goal pursuit.
Theories of Motivation: Ap Psych Motivation And Emotion

Motivation is a complex psychological process that drives our actions and behaviors. Various theories attempt to explain the underlying mechanisms and factors that motivate us. These theories can be broadly classified into biological, psychological, and social perspectives.
Biological Theories
Biological theories focus on the physiological and genetic factors that influence motivation. Key theories include:
- Drive Theory:Asserts that physiological needs (e.g., hunger, thirst) create internal drives that motivate us to seek gratification.
- Incentive Theory:Proposes that external rewards and incentives can motivate behavior by providing positive reinforcement or avoiding punishment.
Psychological Theories
Psychological theories explore the cognitive and emotional factors that shape motivation. Some prominent theories are:
- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs:A hierarchical model that suggests that basic needs (e.g., food, safety) must be met before higher-level needs (e.g., self-esteem, self-actualization) can become motivating.
- Expectancy Theory:Proposes that motivation is influenced by an individual’s expectations about the likelihood of achieving a goal and the value they place on that goal.
Social Theories
Social theories emphasize the role of social factors and interactions in motivation. Key theories include:
- Social Cognitive Theory:Examines how social learning, modeling, and self-efficacy influence motivation.
- Achievement Goal Theory:Focuses on the impact of goals on motivation, distinguishing between performance-oriented and mastery-oriented goals.
Theories of Emotion
Emotions are complex psychological and physiological states that play a significant role in our lives. There are various theories that attempt to explain how emotions arise and how they influence our behavior.
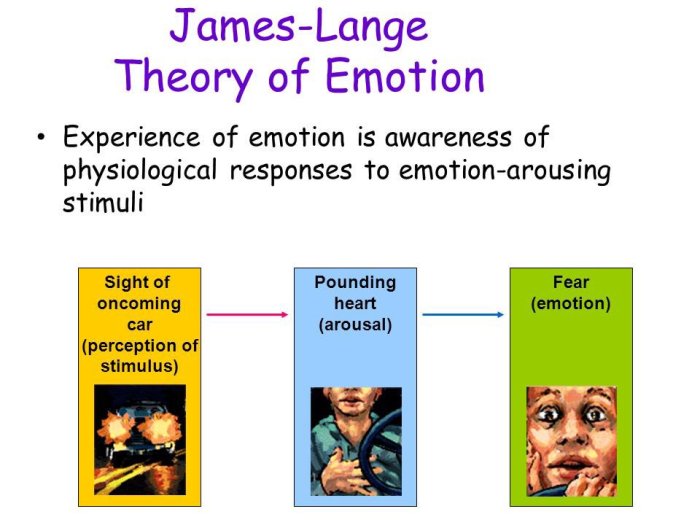
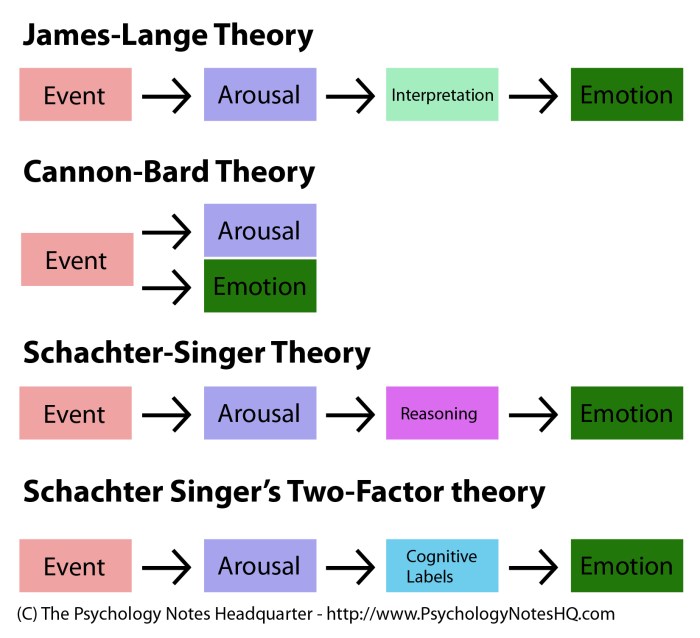
One of the earliest theories of emotion is the James-Lange theory, proposed by William James and Carl Lange. This theory suggests that emotions are primarily physiological responses to external stimuli. According to this theory, when we encounter a stimulus, our bodies react physiologically, and these physiological changes are interpreted as emotions.
For example, when we see a bear, our heart rate increases, our breathing becomes shallow, and our muscles tense up. The James-Lange theory suggests that these physiological changes are what give rise to the emotion of fear.
In contrast to the James-Lange theory, the Cannon-Bard theory, proposed by Walter Cannon and Philip Bard, suggests that emotions and physiological responses occur simultaneously. This theory argues that emotions are not simply the result of physiological changes but rather that both emotions and physiological responses are triggered by the same external stimulus.
For example, when we see a bear, our brain processes the stimulus and triggers both the physiological response (increased heart rate, shallow breathing, tense muscles) and the emotional experience (fear).
In AP Psych, we delve into the intricacies of motivation and emotion. Understanding these concepts is crucial for grasping the complexities of human behavior. Just as a jury evaluates evidence to reach a verdict, in a jury of her peers full text , we can analyze the motivations and emotions of the characters to unravel their actions.
By exploring the interplay between motivation and emotion, we gain a deeper understanding of ourselves and others, a skill that serves us well in both personal and professional endeavors.
The James-Lange theory and the Cannon-Bard theory are just two of the many theories that have been proposed to explain the nature of emotions. While these theories provide different perspectives on how emotions arise, they both highlight the complex interplay between physiological and psychological factors in the experience of emotions.
The Relationship Between Motivation and Emotion
Motivation and emotion are two closely intertwined psychological processes that play a significant role in shaping our behavior. Motivation refers to the internal drives that propel us towards certain goals or actions, while emotion involves the subjective feelings and physiological responses we experience in response to various stimuli.
How Emotions Influence Motivation
- Positive emotions, such as joy and excitement, can energize and enhance motivation. They make us more eager to engage in activities and pursue our goals.
- Negative emotions, such as fear and anger, can dampen motivation. They can lead to avoidance behaviors and make it difficult to focus on our objectives.
- Emotions can influence the intensity of our motivation. For instance, a strong feeling of guilt can provide a powerful motivator to make amends for past actions.
How Motivation Influences Emotion
- Pursuing our goals can evoke various emotions. Achieving a goal can bring joy and satisfaction, while falling short can lead to disappointment and frustration.
- Motivation can shape how we interpret emotional experiences. For example, if we are highly motivated to succeed, we may perceive setbacks as challenges rather than obstacles.
- Motivation can influence the duration and intensity of our emotions. When we are deeply engaged in a motivating activity, we may experience more intense and sustained emotions.
Applications in Psychology

Understanding motivation and emotion is crucial in psychology as it provides insights into human behavior and mental processes. These concepts are widely applied in therapy, education, and other fields to promote well-being and improve outcomes.
Therapy
In therapy, understanding motivation and emotion helps practitioners identify the underlying causes of psychological distress and develop effective interventions. For example, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) focuses on changing maladaptive thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to emotional problems. By understanding the motivations and emotions that drive these patterns, therapists can guide clients towards more positive and healthy coping mechanisms.
Education
In education, understanding motivation and emotion is essential for creating effective learning environments. By recognizing students’ motivations and addressing their emotional needs, educators can foster a supportive and engaging atmosphere that promotes academic success. For instance, teachers may use motivational strategies such as setting achievable goals, providing positive reinforcement, and creating a sense of belonging to enhance student engagement and achievement.
Other Fields
Beyond therapy and education, the understanding of motivation and emotion finds applications in various other fields, including:
- Organizational psychology: Understanding employee motivation and emotion is crucial for enhancing productivity, job satisfaction, and organizational performance.
- Sports psychology: Understanding athletes’ motivations and emotions helps coaches and trainers optimize performance, build team cohesion, and promote mental well-being.
- Health psychology: Understanding the role of motivation and emotion in health behaviors, such as exercise and healthy eating, is essential for promoting healthier lifestyles.
FAQs
What is the key difference between motivation and emotion?
Motivation refers to the internal drive that propels us towards certain actions, while emotion is the subjective experience that accompanies those actions.
How do emotions influence motivation?
Emotions can both enhance and hinder motivation. Positive emotions can provide a boost of energy and drive, while negative emotions can create obstacles and reduce motivation.
Can we control our emotions?
While we cannot always control the emotions we experience, we can learn strategies to manage our emotional responses and prevent them from overwhelming us.

